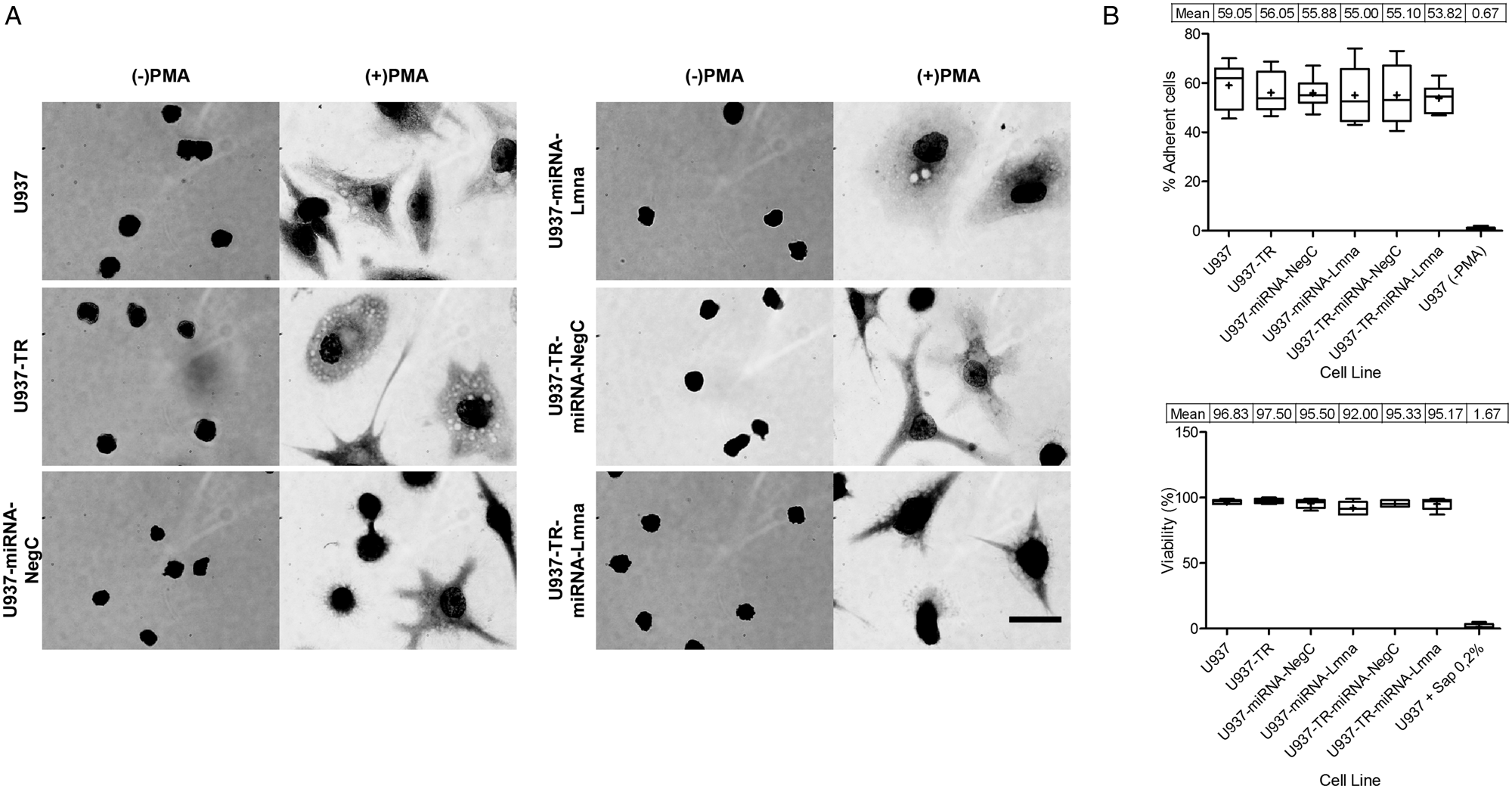
Generation and characterization of U937-TR: a platform cell line for inducible gene expression in human macrophages | Parasitology | Cambridge Core

Morphological changes in (A) non-treated control U937 cells and (B)... | Download Scientific Diagram
Extracellular vesicles of U937 macrophage cell line infected with DENV-2 induce activation in endothelial cells EA.hy926 | PLOS ONE
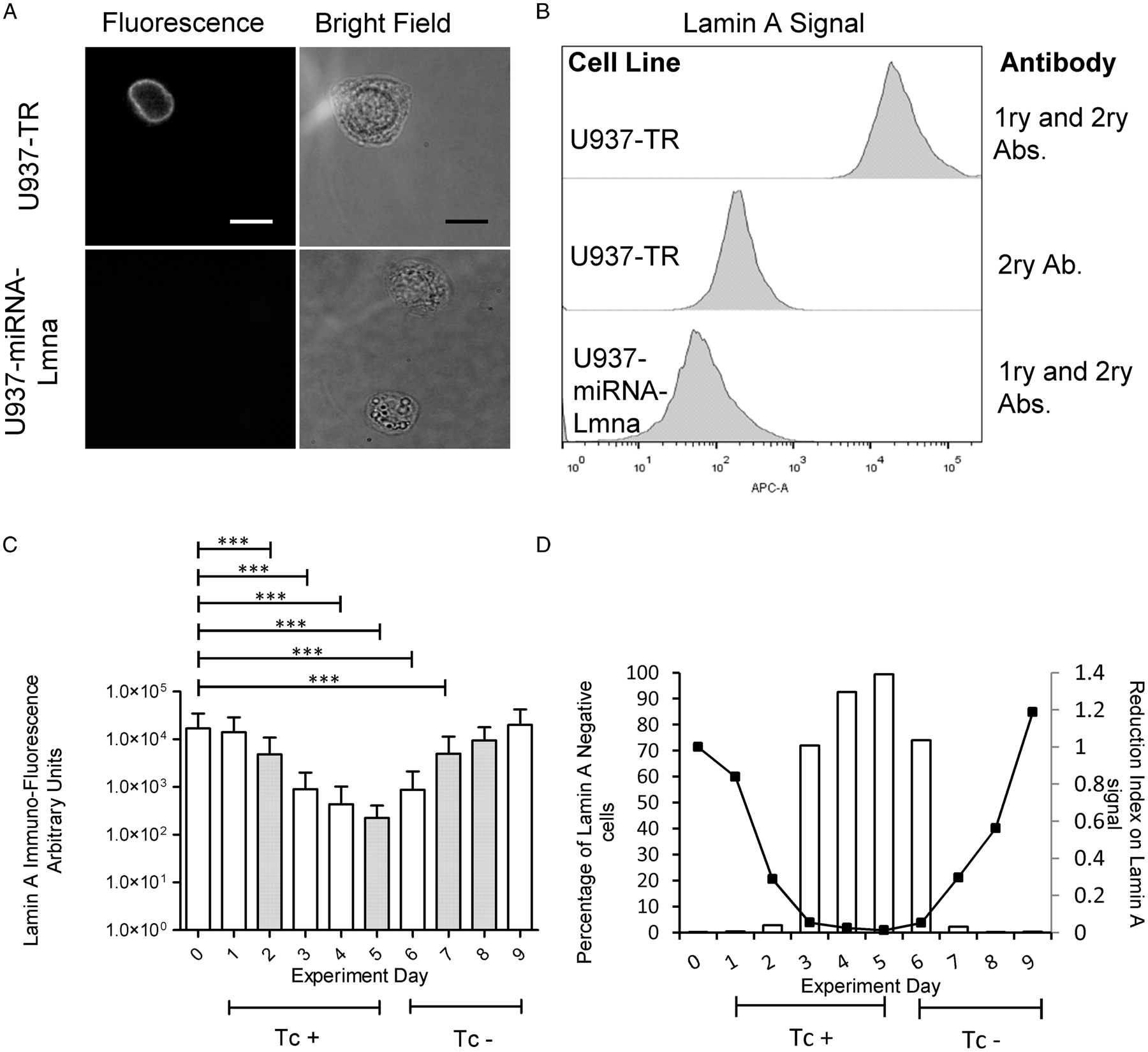
Generation and characterization of U937-TR: a platform cell line for inducible gene expression in human macrophages | Parasitology | Cambridge Core
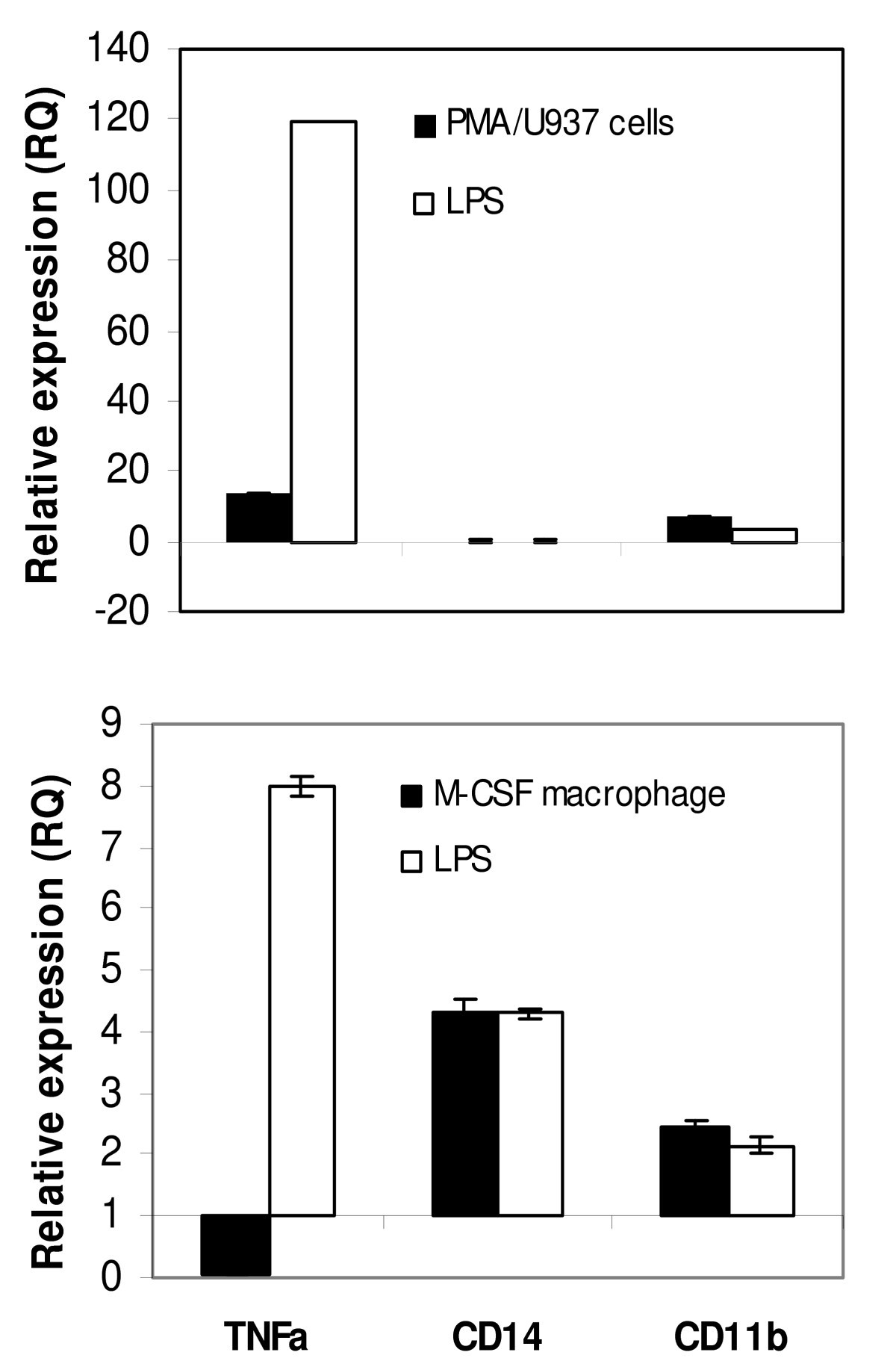
Identification of novel transcriptional regulators involved in macrophage differentiation and activation in U937 cells | BMC Immunology | Full Text

Morphology of U937 cells. A) Control, B) DMSO, C) 1, 25-D3 and D) LPS... | Download Scientific Diagram
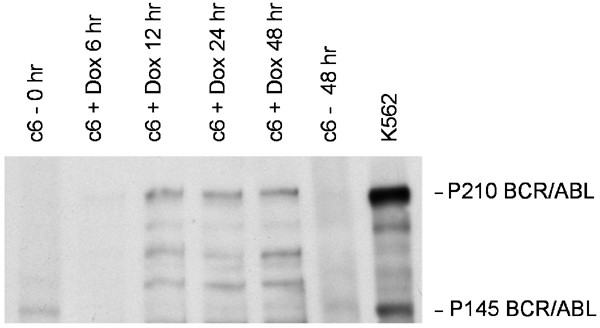
Establishment and phenotypic characterization of human U937 cells with inducible P210 BCR/ABL expression reveals upregulation of CEACAM1 (CD66a) | Leukemia

DIFFERENTIATION OF U-937 MONOCYTES TO MACROPHAGE-LIKE CELLS POLARIZED INTO M1 OR M2 PHENOTYPES ACCORDING TO THEIR SPECIFIC ENVIRONMENT: A STUDY OF MORPHOLOGY, CELL VIABILITY, AND CD MARKERS OF AN IN VITRO MODEL

A) U937 cells form aggregates upon PMA treatment (2–16 nM for 16 h) and... | Download Scientific Diagram

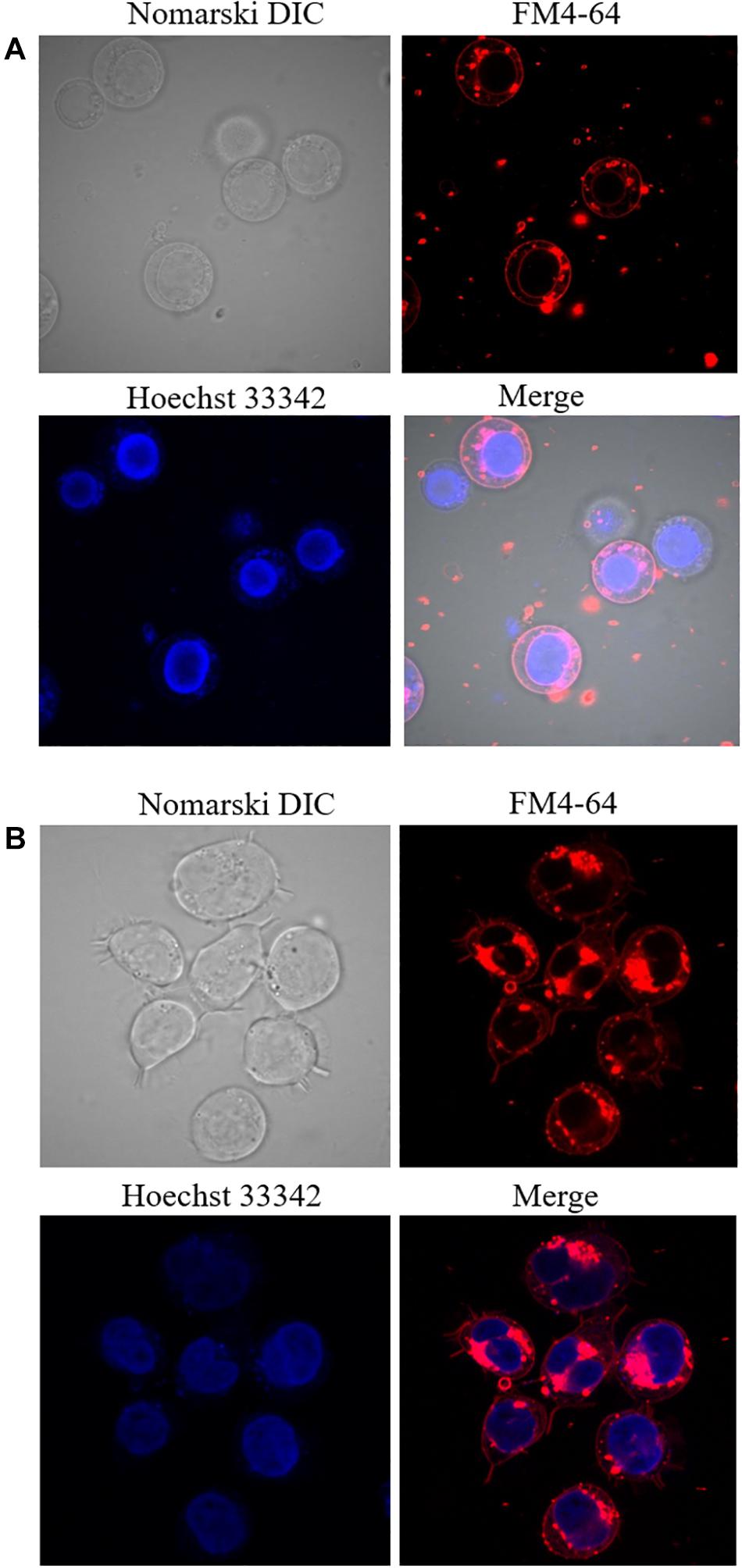






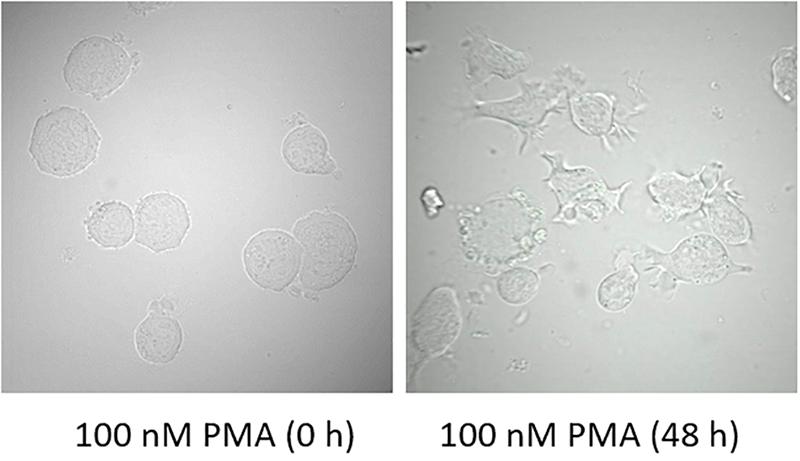
.jpg)